13
13
0
The "Colonel's" Military Pay Through History - Series of Military Pay through the various wars of the United States (World War II - 1941 - 1945)
Prior to World War II, serving in the military wasn't everyone's first choice in career. In 1939, the Army featured a roster of 189,839 servicemen. That changed following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, and by 1945 there were 8,267,958 enlisted.
Salaries vary depending on the source. According to Moneywise, privates were paid $21.00 prior to the US entering the war, a total that increased to $50 in September 1942. The National WWII Museum, on the other hand, lists the average base pay for enlisted servicemen at $71.33, with officers earning a salary of $203.50.
WWII also saw the introduction of Badge Pay for combat infantry members, due to the hazardous conditions they fought in. The initiative awarded $10.00 a month to holders of the Combat Infantryman's Badge, earned through combat service, while those with the Expert Infantryman's Badge, earned through proficiency training, were given $5.00.
American soldiers were quite well-paid in comparison to civilians. The United States Army (including the Army Air Forces), Navy, and the Marine Corps all utilized the same pay scale in WWII.
After the passage of the Pay Readjustment Act of 1942 on 16 June 1942 which redefined the pay scales of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard, the average American serviceman who was single made a base pay of $50.00 per month, or $600.00 per year before any spending. Accounting for the man being in the military, (and not having to pay taxes if their yearly income was under $1,500.00, or buy luxury or necessity items that were provided automatically in most cases by the military such as food, clothes or soap) that would scale out to a net annual pay of about $3,600.00 "civilian" dollars in 1944. In 1944, an annual income of $3,600.00 was more than 80 percent of all single workers in the United States.
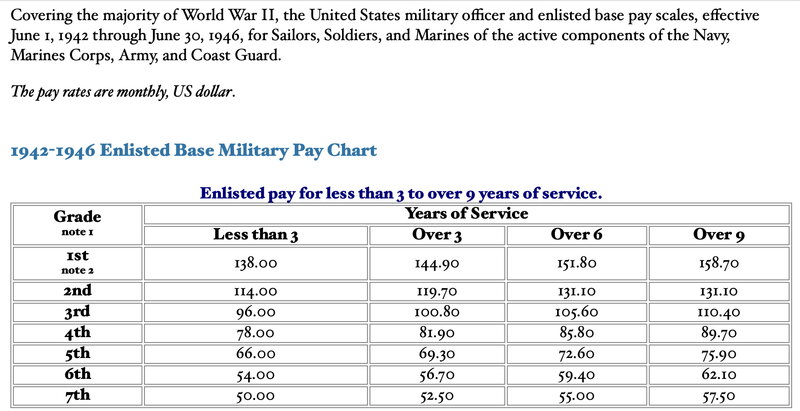
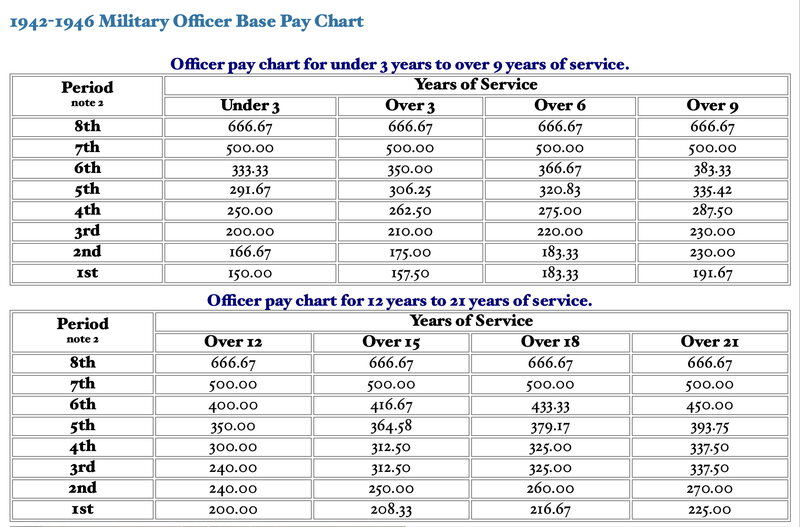
See Pictures Below in the Response Section for the Pay Charts by Enlisted and Officers
Women in the military were awarded the same pay as men.
Soldiers holding any of the five general officer ranks received a base pay and did not experience this five-percent increase, no matter how many years they served. If an officer stayed at a rank for a set amount of time, (5 years for 2nd lieutenants or equivalent, 10 years for 1st lieutenants or equivalent, 17 years for captains or equivalent, 23 years for majors or equivalent, and 30 years for lieutenant colonels or equivalent) he was then entitled to the pay of the next-highest officer rank.
If a soldier had dependents, such as children, a wife, brothers or sisters, or parents he needed to support, he would receive additional pay; see my third link for the complicated chart. For service overseas, including in Alaska, base pay at each rank was increased 20 percent.
If a soldier was awarded the Medal of Honor, the Distinguished Service Cross, the Distinguished Service Medal, or the Soldier's Medal, he would earn an extra $2.00 per month. Each additional award of the above medals netted another $2.00 bonus per month.
Air Corps men who were qualified to fly or took regular flights received an additional pay per month amounting to 50 percent of their base pay. Enlisted paratroopers or paratroopers-in-training received an additional pay of $50.00 per month, no matter their base pay; officers received $100.00. This is what you were alluding to. Glider troops initially did not receive the $50.00 or $100.00 hazard pay. After various assaults proved that landing via glider was just as dangerous, if not more dangerous, than parachuting, a hazard pay of $25.00 per month for enlisted glider troops and $50.00 for officers was instituted.
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies and the Axis powers. Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising their resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks and aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the deadliest conflict in history, causing the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Germany, Austria, Japan, and Korea were occupied, and German and Japanese leaders were put on trial for war crimes.
The causes of World War II included unresolved tensions in the aftermath of World War I, the rise of fascism in Europe and militarism in Japan. Key events preceding the war included Japan's invasion of Manchuria in 1931, the Spanish Civil War, the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937, and Germany's annexations of Austria and the Sudetenland. World War II is generally considered to have begun on 1 September 1939, when Nazi Germany, under Adolf Hitler, invaded Poland, after which the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany. Poland was also invaded by the Soviet Union in mid-September, and was partitioned between Germany and the Soviet Union under the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact. In 1940, the Soviet Union annexed the Baltic states and parts of Finland and Romania, while Germany conquered Norway, Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. After the fall of France in June 1940, the war continued mainly between Germany, now assisted by Fascist Italy, and the British Empire, with fighting in the Balkans, Mediterranean, and Middle East, East Africa, the aerial Battle of Britain and the Blitz, and the naval Battle of the Atlantic. By mid-1941 Yugoslavia and Greece had also been defeated by Axis countries. In June 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union, opening the Eastern Front and initially making large territorial gains along with Axis allies.
In December 1941, Japan attacked American and British territories in Asia and the Pacific, including Pearl Harbor in Hawaii, leading the United States to enter the war against the Axis. Japan conquered much of coastal China and Southeast Asia, but its advances in the Pacific were halted in June 1942 at the Battle of Midway. In early 1943, Axis forces were defeated in North Africa and at Stalingrad in the Soviet Union. An Allied invasion of Italy in July resulted in the fall of its fascist regime, and Allied offensives in the Pacific and the Soviet Union forced the Axis to retreat on all fronts. In 1944, the Western Allies invaded France at Normandy, the Soviet Union advanced into central Europe, and the US crippled Japan's navy and captured key Pacific islands.
The war in Europe concluded with the liberation of German-occupied territories and the invasion of Germany by the Allies which culminated in the fall of Berlin to Soviet troops, and Germany's unconditional surrender on 8 May 1945. On 6 and 9 August, the US dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan. Faced with an imminent Allied invasion, the prospect of further atomic bombings, and a Soviet declaration of war and invasion of Manchuria, Japan announced its unconditional surrender on 15 August, and signed a surrender document on 2 September 1945.
World War II transformed the political, economic, and social structures of the world, and established the foundation of international relations for the rest of the 20th century and into the 21st century. The United Nations was created to foster international cooperation and prevent future conflicts, with the victorious great powers—China, France, the Soviet Union, the UK, and the US—becoming the permanent members of its security council. The Soviet Union and the US emerged as rival superpowers, setting the stage for the half-century Cold War. In the wake of Europe's devastation, the influence of its great powers waned, triggering the decolonisation of Africa and of Asia. Many countries whose industries had been damaged moved towards economic recovery and expansion.
Prior to World War II, serving in the military wasn't everyone's first choice in career. In 1939, the Army featured a roster of 189,839 servicemen. That changed following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, and by 1945 there were 8,267,958 enlisted.
Salaries vary depending on the source. According to Moneywise, privates were paid $21.00 prior to the US entering the war, a total that increased to $50 in September 1942. The National WWII Museum, on the other hand, lists the average base pay for enlisted servicemen at $71.33, with officers earning a salary of $203.50.
WWII also saw the introduction of Badge Pay for combat infantry members, due to the hazardous conditions they fought in. The initiative awarded $10.00 a month to holders of the Combat Infantryman's Badge, earned through combat service, while those with the Expert Infantryman's Badge, earned through proficiency training, were given $5.00.
American soldiers were quite well-paid in comparison to civilians. The United States Army (including the Army Air Forces), Navy, and the Marine Corps all utilized the same pay scale in WWII.
After the passage of the Pay Readjustment Act of 1942 on 16 June 1942 which redefined the pay scales of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard, the average American serviceman who was single made a base pay of $50.00 per month, or $600.00 per year before any spending. Accounting for the man being in the military, (and not having to pay taxes if their yearly income was under $1,500.00, or buy luxury or necessity items that were provided automatically in most cases by the military such as food, clothes or soap) that would scale out to a net annual pay of about $3,600.00 "civilian" dollars in 1944. In 1944, an annual income of $3,600.00 was more than 80 percent of all single workers in the United States.
See Pictures Below in the Response Section for the Pay Charts by Enlisted and Officers
Women in the military were awarded the same pay as men.
Soldiers holding any of the five general officer ranks received a base pay and did not experience this five-percent increase, no matter how many years they served. If an officer stayed at a rank for a set amount of time, (5 years for 2nd lieutenants or equivalent, 10 years for 1st lieutenants or equivalent, 17 years for captains or equivalent, 23 years for majors or equivalent, and 30 years for lieutenant colonels or equivalent) he was then entitled to the pay of the next-highest officer rank.
If a soldier had dependents, such as children, a wife, brothers or sisters, or parents he needed to support, he would receive additional pay; see my third link for the complicated chart. For service overseas, including in Alaska, base pay at each rank was increased 20 percent.
If a soldier was awarded the Medal of Honor, the Distinguished Service Cross, the Distinguished Service Medal, or the Soldier's Medal, he would earn an extra $2.00 per month. Each additional award of the above medals netted another $2.00 bonus per month.
Air Corps men who were qualified to fly or took regular flights received an additional pay per month amounting to 50 percent of their base pay. Enlisted paratroopers or paratroopers-in-training received an additional pay of $50.00 per month, no matter their base pay; officers received $100.00. This is what you were alluding to. Glider troops initially did not receive the $50.00 or $100.00 hazard pay. After various assaults proved that landing via glider was just as dangerous, if not more dangerous, than parachuting, a hazard pay of $25.00 per month for enlisted glider troops and $50.00 for officers was instituted.
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies and the Axis powers. Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising their resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks and aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the deadliest conflict in history, causing the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Germany, Austria, Japan, and Korea were occupied, and German and Japanese leaders were put on trial for war crimes.
The causes of World War II included unresolved tensions in the aftermath of World War I, the rise of fascism in Europe and militarism in Japan. Key events preceding the war included Japan's invasion of Manchuria in 1931, the Spanish Civil War, the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937, and Germany's annexations of Austria and the Sudetenland. World War II is generally considered to have begun on 1 September 1939, when Nazi Germany, under Adolf Hitler, invaded Poland, after which the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany. Poland was also invaded by the Soviet Union in mid-September, and was partitioned between Germany and the Soviet Union under the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact. In 1940, the Soviet Union annexed the Baltic states and parts of Finland and Romania, while Germany conquered Norway, Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. After the fall of France in June 1940, the war continued mainly between Germany, now assisted by Fascist Italy, and the British Empire, with fighting in the Balkans, Mediterranean, and Middle East, East Africa, the aerial Battle of Britain and the Blitz, and the naval Battle of the Atlantic. By mid-1941 Yugoslavia and Greece had also been defeated by Axis countries. In June 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union, opening the Eastern Front and initially making large territorial gains along with Axis allies.
In December 1941, Japan attacked American and British territories in Asia and the Pacific, including Pearl Harbor in Hawaii, leading the United States to enter the war against the Axis. Japan conquered much of coastal China and Southeast Asia, but its advances in the Pacific were halted in June 1942 at the Battle of Midway. In early 1943, Axis forces were defeated in North Africa and at Stalingrad in the Soviet Union. An Allied invasion of Italy in July resulted in the fall of its fascist regime, and Allied offensives in the Pacific and the Soviet Union forced the Axis to retreat on all fronts. In 1944, the Western Allies invaded France at Normandy, the Soviet Union advanced into central Europe, and the US crippled Japan's navy and captured key Pacific islands.
The war in Europe concluded with the liberation of German-occupied territories and the invasion of Germany by the Allies which culminated in the fall of Berlin to Soviet troops, and Germany's unconditional surrender on 8 May 1945. On 6 and 9 August, the US dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan. Faced with an imminent Allied invasion, the prospect of further atomic bombings, and a Soviet declaration of war and invasion of Manchuria, Japan announced its unconditional surrender on 15 August, and signed a surrender document on 2 September 1945.
World War II transformed the political, economic, and social structures of the world, and established the foundation of international relations for the rest of the 20th century and into the 21st century. The United Nations was created to foster international cooperation and prevent future conflicts, with the victorious great powers—China, France, the Soviet Union, the UK, and the US—becoming the permanent members of its security council. The Soviet Union and the US emerged as rival superpowers, setting the stage for the half-century Cold War. In the wake of Europe's devastation, the influence of its great powers waned, triggering the decolonisation of Africa and of Asia. Many countries whose industries had been damaged moved towards economic recovery and expansion.
Edited 1 d ago
Posted 3 d ago
Responses: 6
Posted 2 d ago
While in Bootcamp in 1964, it was still 50 dollars a month. As an E-5 over three and one-half years in the Corps, including combat pay, I received a little more than four hundred dollars a month. When they got the large pay increases, they took many of the perks we had. Anyone willing to fight and die if necessary deserves both. Due to the increasing chaos in the world and our government, they are definitely underpaid.
(4)
Comment
(0)
Read This Next








 WWII World War Two
WWII World War Two Military Pay
Military Pay Military History
Military History